How Solar Hot Water Systems Work: Components, Benefits & Maintenance
Solar hot water systems offer an energy-efficient and environmentally friendly way to heat water using the power of the sun. Whether you’re looking to save on energy bills or lower your carbon footprint, understanding how these systems work can help you make the most of your investment.
☀️ What Is a Solar Hot Water System?
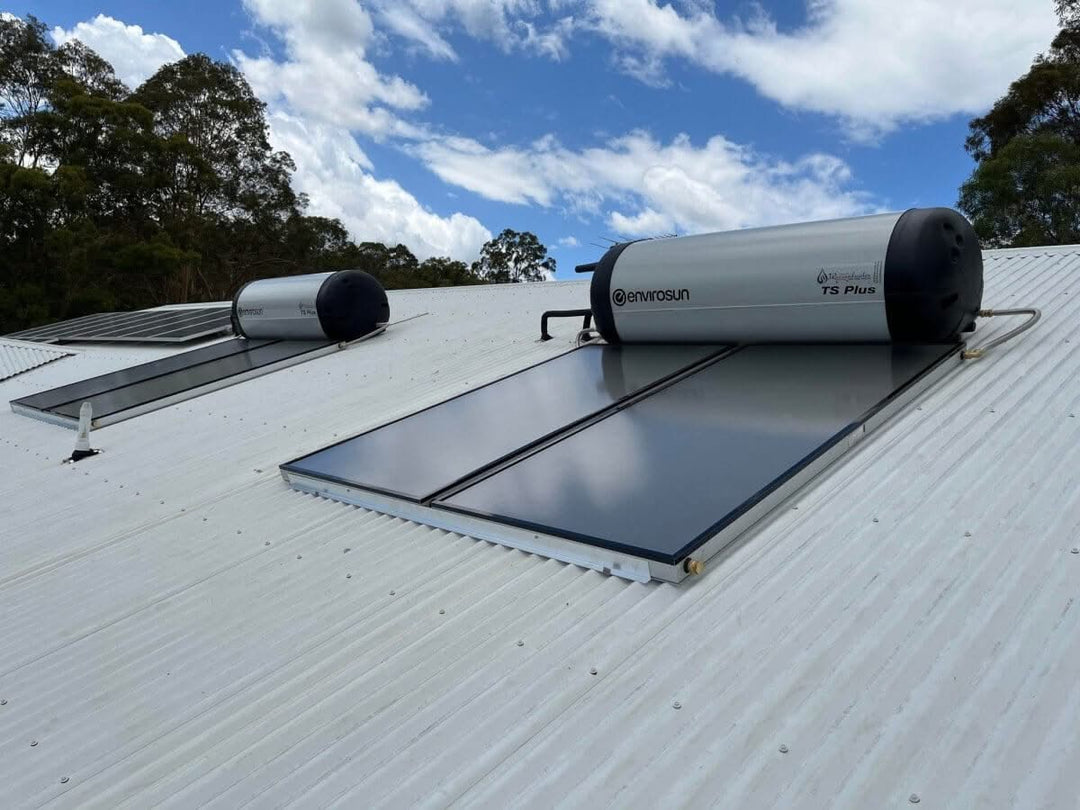
A solar hot water system captures solar energy and converts it into heat to warm water for household use. These systems are commonly installed on rooftops and are ideal for sunny climates like Brisbane and the Gold Coast.
Systems come in two main types:
-
Active systems, which use pumps and controllers to circulate water
-
Passive systems, which rely on gravity and natural convection
🔧 Key Components of a Solar Hot Water System
1. Solar Collector
This is the heart of the system where sunlight is absorbed and turned into heat.
🔹 Flat Plate Collectors
-
Glazed box with a black absorber plate
-
Water runs through pipes beneath the plate and heats up
-
Best for warmer regions with consistent sunlight
🔹 Evacuated Tube Collectors
-
Rows of sealed glass tubes with a vacuum inside
-
More efficient in colder or overcast areas
-
Great for year-round hot water, even in winter
👉 See our range of solar hot water systems including flat plate and evacuated tube options.
2. Storage Tank
-
Insulated tank that stores the heated water
-
Often mounted on the roof or at ground level
-
Made from stainless steel or glass-lined steel
-
Sizes range from 160L to 400L+ depending on household size
3. Heat Exchanger
Transfers heat from the solar collector to the water in the tank.
-
Essential for indirect systems that use antifreeze
-
Keeps water safe and separate from the collector fluid
4. Pump (Active Systems Only)
-
Moves water between the collector and tank
-
Operates based on temperature differences
-
Ensures steady hot water supply even during high usage periods
5. Controller
-
Turns the pump on/off based on temperature readings
-
Prevents overheating and freezing
-
Ensures system efficiency year-round
🏗️ Installation & Maintenance
Installation
Professional installation is key to long-term system performance:
-
Collector is mounted on a north-facing roof or ground frame
-
Insulated pipes connect the tank and collector
-
A backup electric or gas booster is installed for cloudy days
-
Controller and pump are set up for automatic operation
Need expert installation? Book with JR Gas & Water — your solar hot water specialists.
Maintenance
Solar systems require minimal upkeep but still benefit from:
-
Annual inspection of pipes and valves
-
Cleaning the collector surface to remove dirt
-
Checking pump and controller function
-
Replacing antifreeze fluid in indirect systems
-
Testing the pressure relief valve for safety
✅ Benefits of Solar Hot Water Systems
-
Save on Bills: Slash electricity or gas use for water heating
-
Eco-Friendly: Reduces your home’s carbon footprint
-
Low Maintenance: Few moving parts = fewer problems
-
Long Lifespan: Can last over 15 years with proper care
-
Adds Value: Increases your property’s sustainability appeal
Looking to upgrade? Check out systems like the
🧰 Final Thoughts
Solar hot water systems are a smart investment for homes and businesses across Queensland. With the right components and proper installation, you'll enjoy free hot water from the sun and long-term savings on utility bills.
🔥 Ready to switch to solar?
Get a quote today from JR Gas & Water — voted Best Plumbers & Home Care Store 2023, 2024 & 2025.
We supply and install premium solar systems with honest pricing, expert service, and fast turnaround.
☀️ Hot water. Powered by sunshine.